The Generative AI shift: Angelini Industries’ approach
Written by Carlo Torniai, Group Chief Data & Analytics Officer, Angelini Industries
Share

What is Artificial Intelligence?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) encompasses a wide range of definitions. Among them is the "classic" definition by Russell and Norvig (S. Russell, P. Norvig in Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach), which describes it as "the study of agents that receive perceptions from the environment and perform actions." As noted by Wikipedia, a broader definition defines AI as "the ability of computational systems to carry out tasks typically associated with human intelligence, such as learning, reasoning, problem-solving, perception, and decision-making."
These definitions underscore a fundamental aspect of AI: its capacity to learn, adapt, and improve its performance through interactions with data and the surrounding environment.
Operating principles: from Expert Systems to Generative AI
AI technologies can primarily be categorized into three main groups, reflecting their chronological evolution:
- Expert Systems: systems based on symbolic rule-based logic (e.g., if a condition is met, assign a value to a variable), which are designed to emulate complex human reasoning processes.
- Machine Learning: algorithms capable of autonomously learning patterns and rules from data, progressively improving their performance through experience.
- Deep Learning: a specialized branch of Machine Learning that employs advanced neural network architectures to extract insights from large, heterogeneous datasets including images, video, and other unstructured formats.
This progression marks the shift from manually encoded logic to data-driven learning systems, ultimately paving the way for today’s Generative AI technologies.
Generative AI represents the most recent advancement in the field of Deep Learning. These algorithms are capable of creating entirely new and original content such as text, images, video, audio, code, or synthetic data based on a textual "prompt." Unlike traditional AI, which focuses on interpreting, processing, and classifying existing information, Generative AI is designed to produce brand-new outputs.
How companies are using Generative AI
Businesses are increasingly leveraging Generative AI across a range of operational areas, including:
- Productivity: assisting with daily tasks and improving access to company knowledge bases.
- Technical Support & Customer Care: enhancing customer service through faster and more accurate responses.
- Marketing & Communication: enabling quick, personalized creation of targeted promotional materials.
- Legal: streamlining contract management and delivering fast, precise document reviews.
- Research & Development: speeding up the design and iteration of new products and solutions.
One of the most promising applications of Generative AI is in the pharmaceutical industry, where it can generate new molecules in silico, design more efficient clinical trials, and accelerate early-stage analysis drastically reducing the time required to develop new drugs ("Generative AI in the pharmaceutical industry" (2024)).
Challenges in implementing Generative AI
The adoption of Generative AI also brings with it specific challenges and critical issues, including:
- Compliance with regulations and copyright: ensuring that generated content aligns with legal frameworks, particularly the AI Act.
- Data privacy and security: enforcing strict adherence to data protection standards, such as the GDPR.
- Output control: maintaining high standards of quality and reliability while minimizing issues such as “hallucinations” (incorrect or fabricated model outputs).
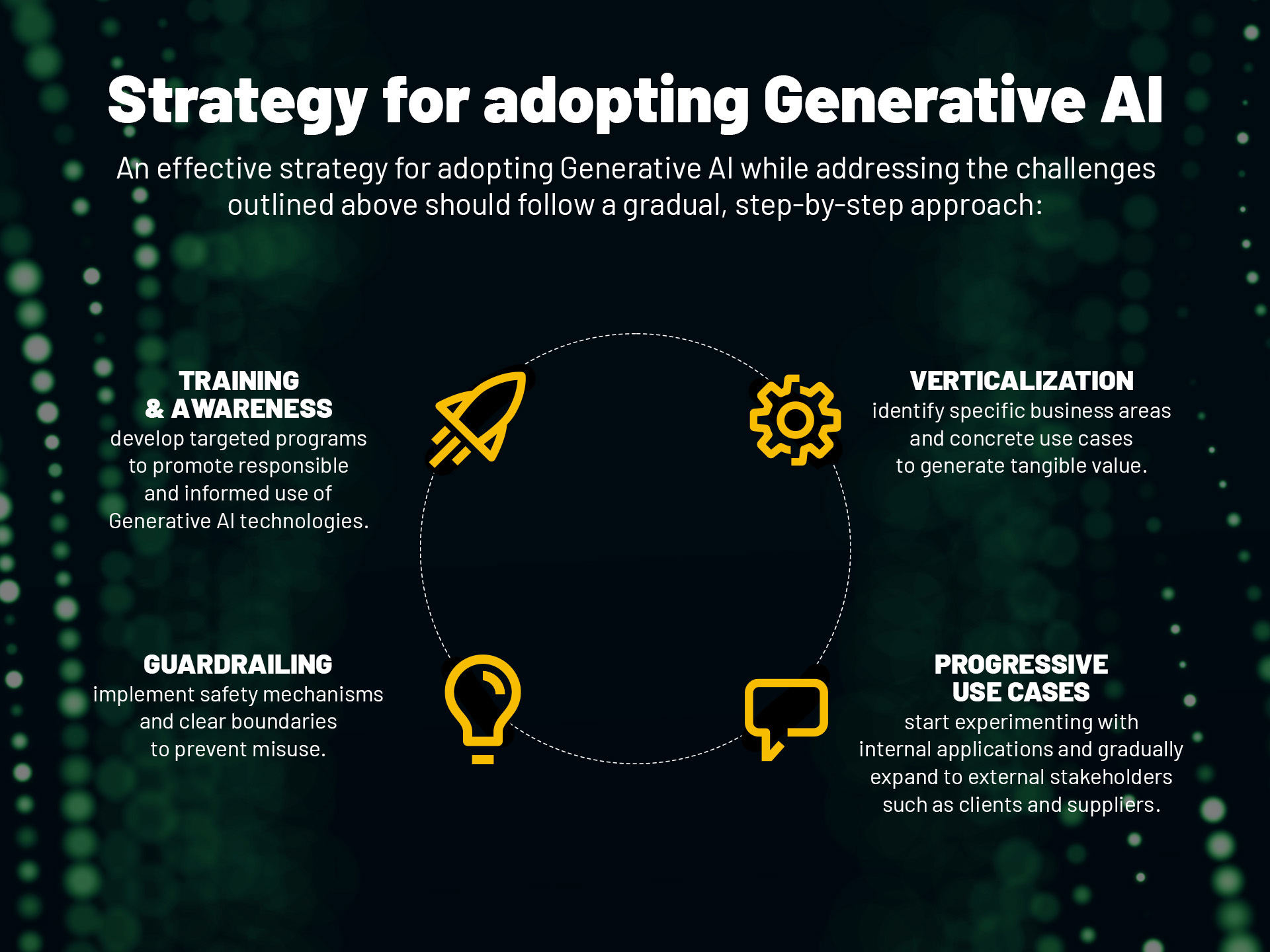
An effective strategy for adopting Generative AI while addressing the challenges outlined above should follow a gradual, step-by-step approach:
- Training and awareness: develop targeted programs to promote responsible and informed use of Generative AI technologies.
- Guardrailing: implement safety mechanisms and clear boundaries to prevent misuse.
- Verticalization: identify specific business areas and concrete use cases to generate tangible value.
- Progressive use cases: start experimenting with internal applications and gradually expand to external stakeholders such as clients and suppliers.
Angelini Industries adopted this incremental approach by launching a company-wide training program during the summer of 2023. This initiative culminated in the release of AskAI: a “general-purpose” Generative AI platform developed in-house to boost individual productivity. The system was built with a security-by-design approach, with a strong focus on protecting sensitive corporate data. Building on AskAI, several vertical applications have since been developed, from creating topic-specific knowledge bases to support resolving technical tickets to suggestions for troubleshooting production line downtimes and even assistance drafting patent applications.
Looking Ahead
According to the Boston Consulting Group (AI Radar, January 2025), investments in Generative AI are expected to grow by 60% over the next three years, driving the development of more specialized, compact, and sustainable models capable of running on mobile devices with minimal computational impact. At the same time, we will witness the evolution of so-called Agentic AI, where multiple autonomous "agents" collaborate to automate complex tasks and deliver personalized solutions.
However, Generative AI is not merely a technological innovation but represents a profound cultural and organizational shift. As McKinsey highlights, "the real value of AI comes from the radical redesign of organizational and business processes."
Angelini Industries' experience demonstrates that a conscious, inclusive, and strategic approach can be a powerful lever for sustainable growth and business competitiveness.
 Angelini Industries
Angelini Industries




